
Scroll views in SwiftUI are very straight-forward but give us no information or control over the current position of its content. So how can we detect for instance that the user has scrolled beyond certain threshold off the top?
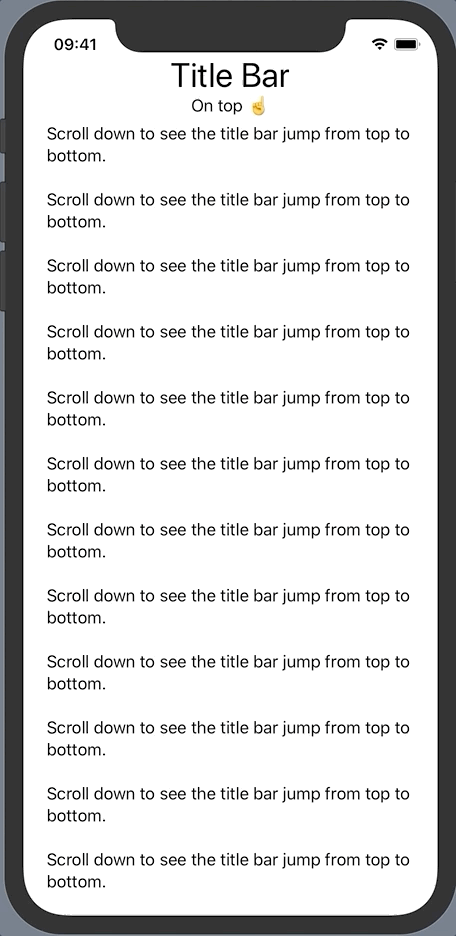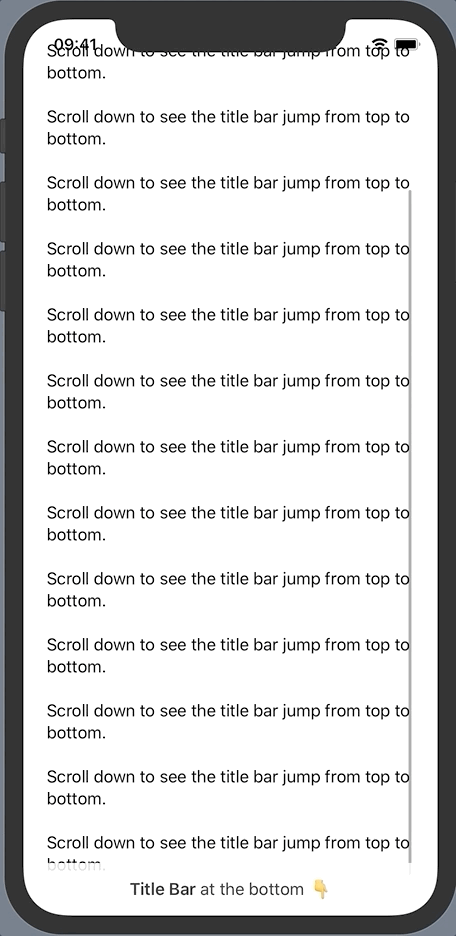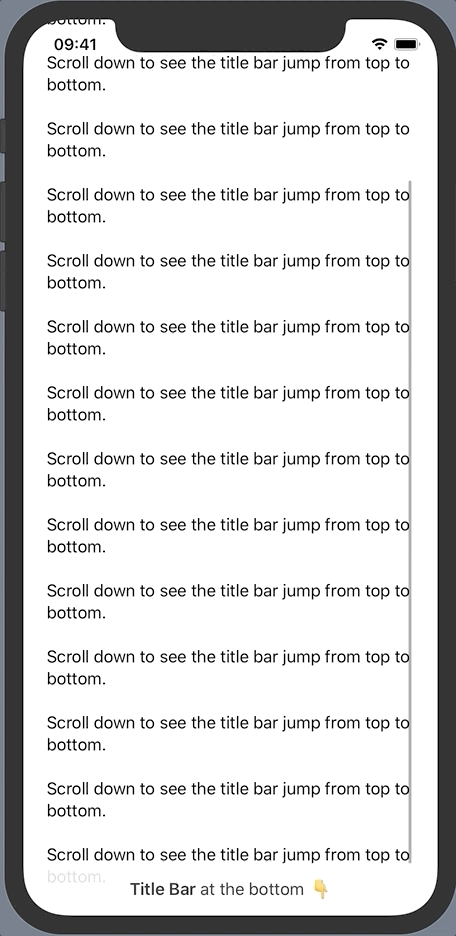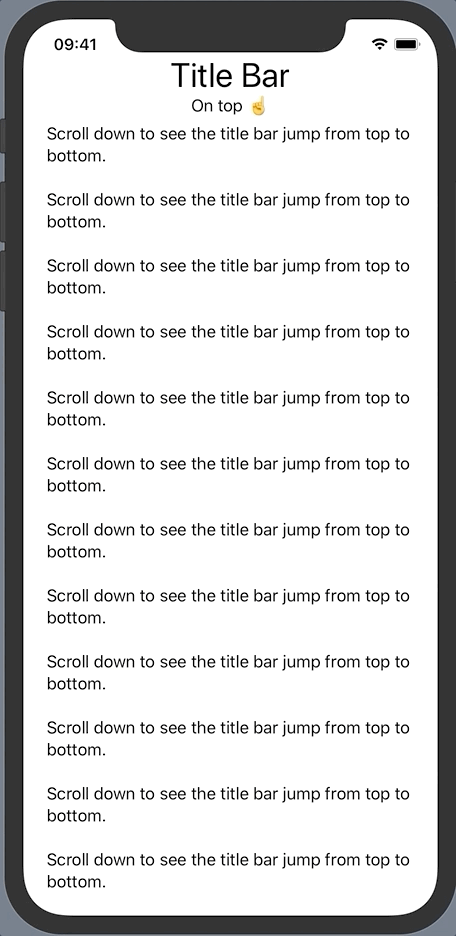
Suppose we have some scrollable content with a title bar that is outside the ScrollView.
public struct JumpingTitleBar: View {
var scrollView: some View {
ScrollView(.vertical) {
Text("""
Scroll down to see the title bar jump from top to bottom.
…
""")
}
}
var topBar: some View { … }
var bottomBar: some View { … }
var body: some View {
ZStack {
scrollView
VStack {
topBar
Spacer()
bottomBar
}
}
}
}We want the title bar to jump to the bottom once the user started scrolling down the text. Let’s start by adding an onTop state variable to represent this behavior.
@State var onTop = true
var body: some View {
ZStack {
scrollView
VStack {
if onTop { topBar }
Spacer()
if !onTop { bottomBar }
}
}
}Now for the magic bit of the article, how do we actually find out what the offset of the contents is at all times? For this we leverage .anchorPreference.
Anchor preferences let us compile geometry data about our descendants, of which our scrollable Text is part. We start by defining the key type with a default value and a reducer.
struct OffsetKey: PreferenceKey {
static var defaultValue: CGFloat = 0
static func reduce(value: inout CGFloat, nextValue: () -> CGFloat) {
value = nextValue()
}
}From the text view itself we report our top anchor’s y position to our ancestors.
GeometryReader { g in
ScrollView(.vertical) {
Text(…)
.anchorPreference(key: OffsetKey.self, value: .top) {
g[$0].y
}
…We will catch the offset value on the flip side using the onPreferenceChange() modifier on the scroll view itself.
var body: some View {
ZStack {
scrollView
.onPreferenceChange(OffsetKey.self) {
…
}
…At this point the only thing remaining is to update our internal state according to the received offset.
…
scrollView
.onPreferenceChange(OffsetKey.self) {
if $0 < -10 {
self.onTop = false
} else {
self.onTop = true
}
}
…The title bar now slides away shortly after we start scrolling down and the footer instantly fades in. The whole action reverses when scrolling all the way back to the top.
For sample code featuring this and other techniques please checkout our working examples repo.